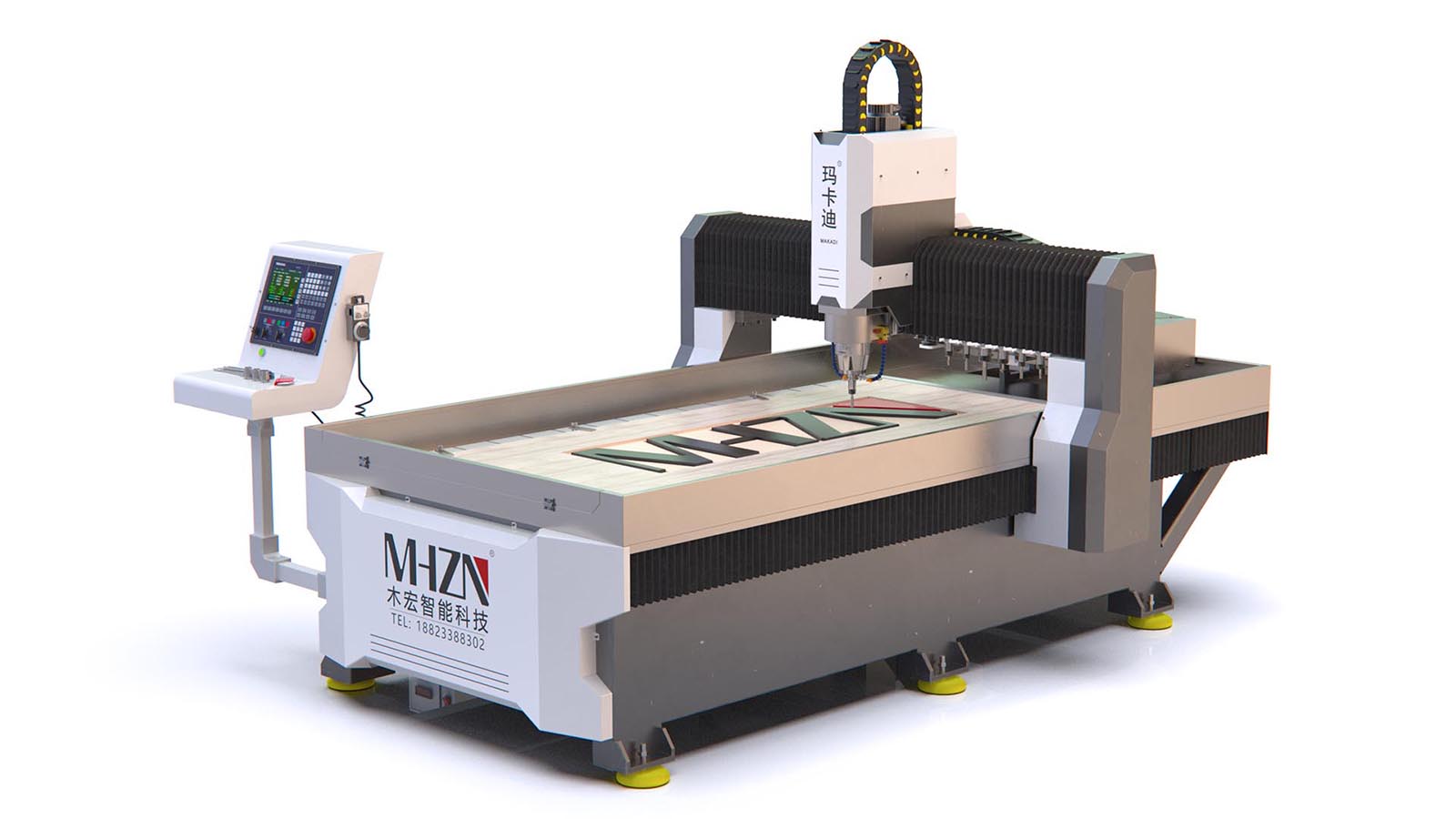
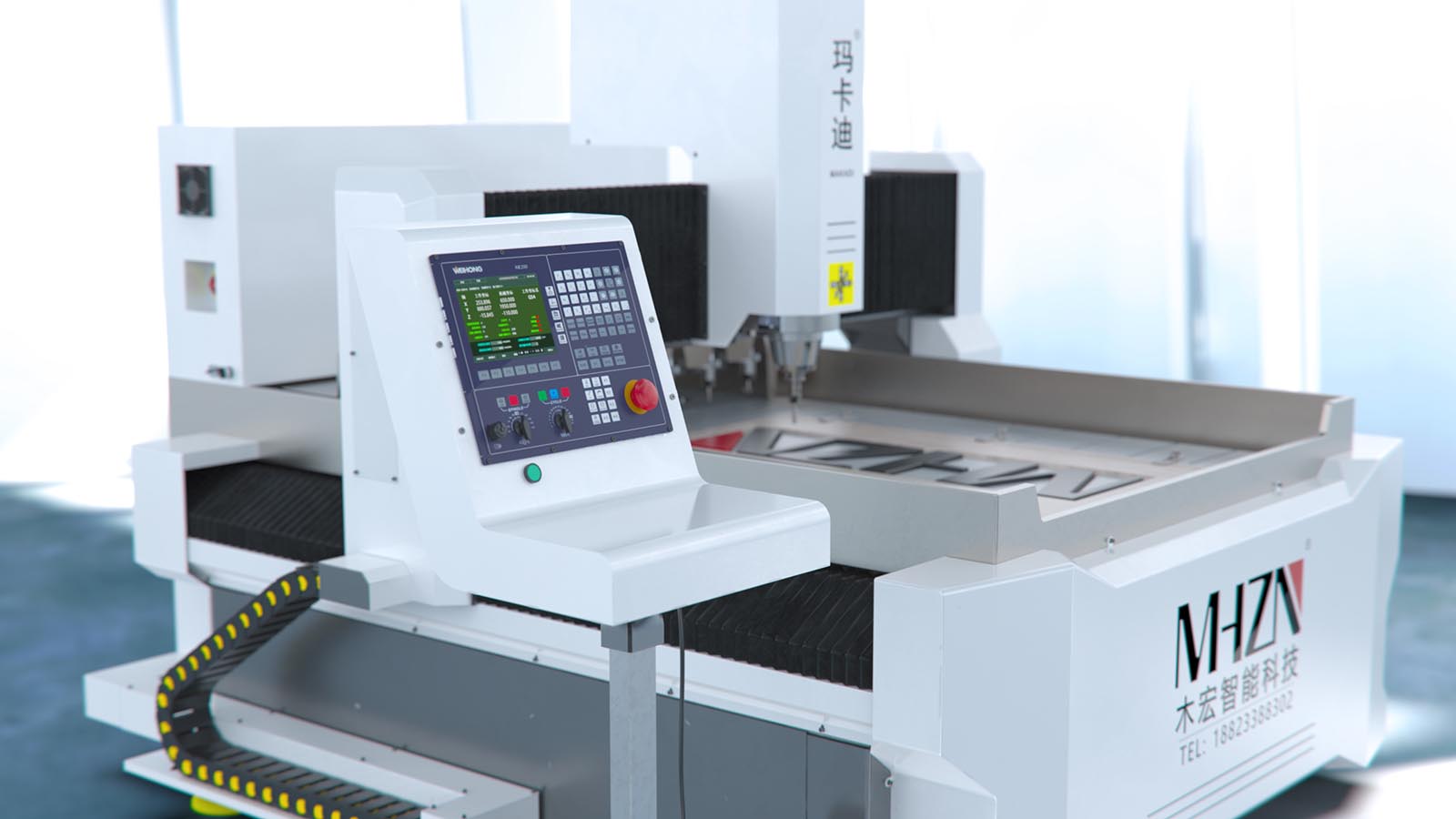
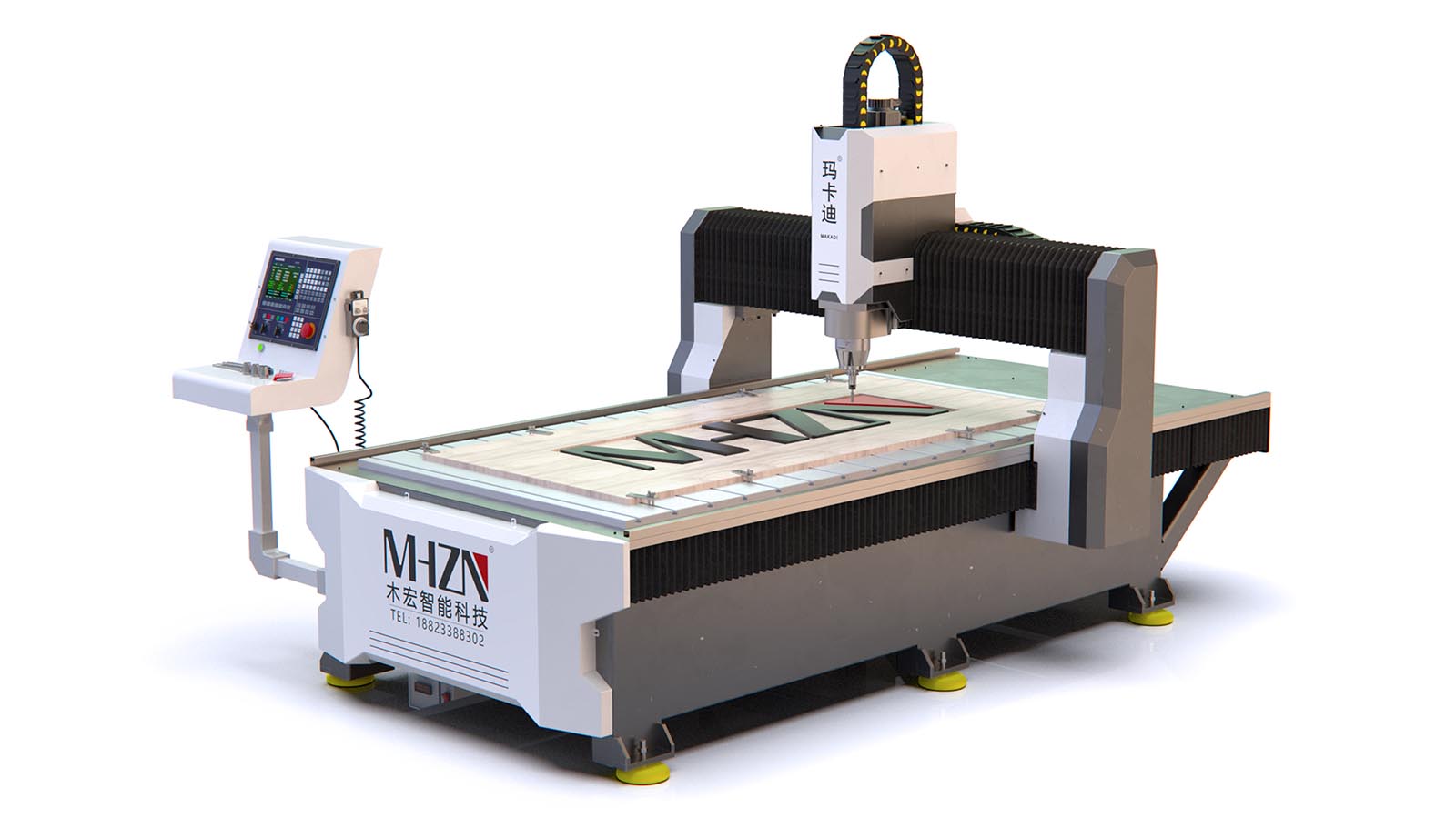
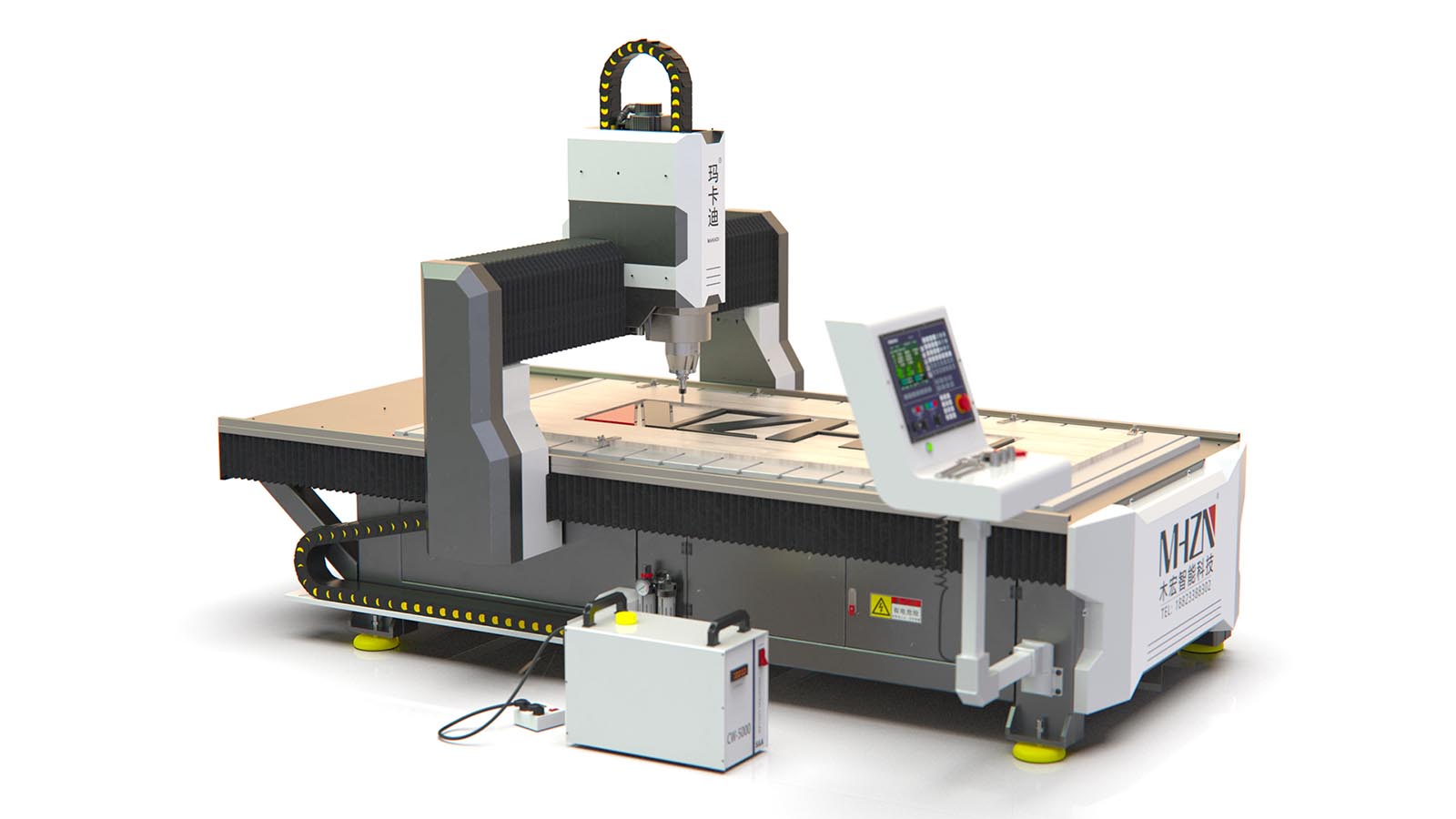
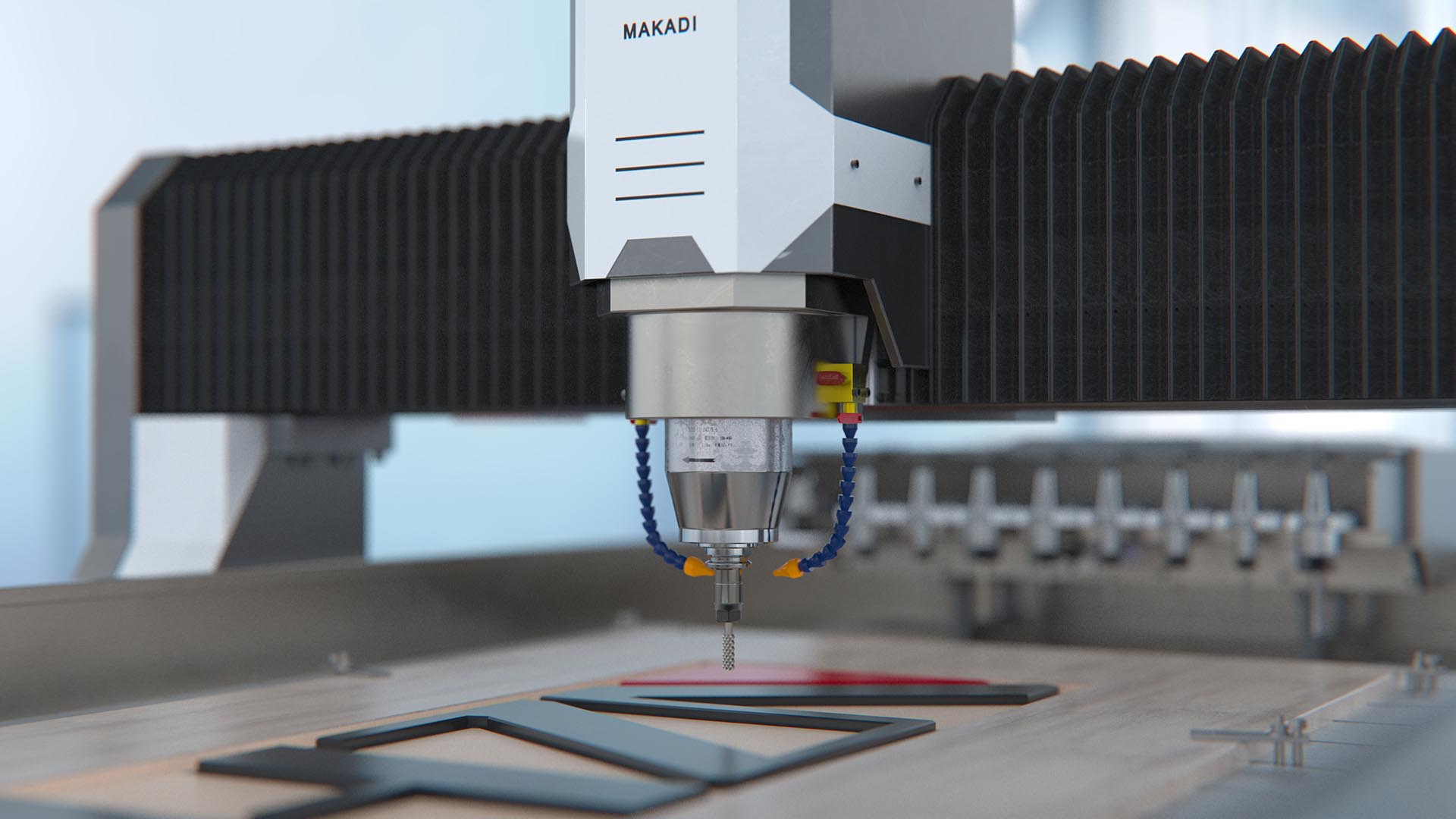
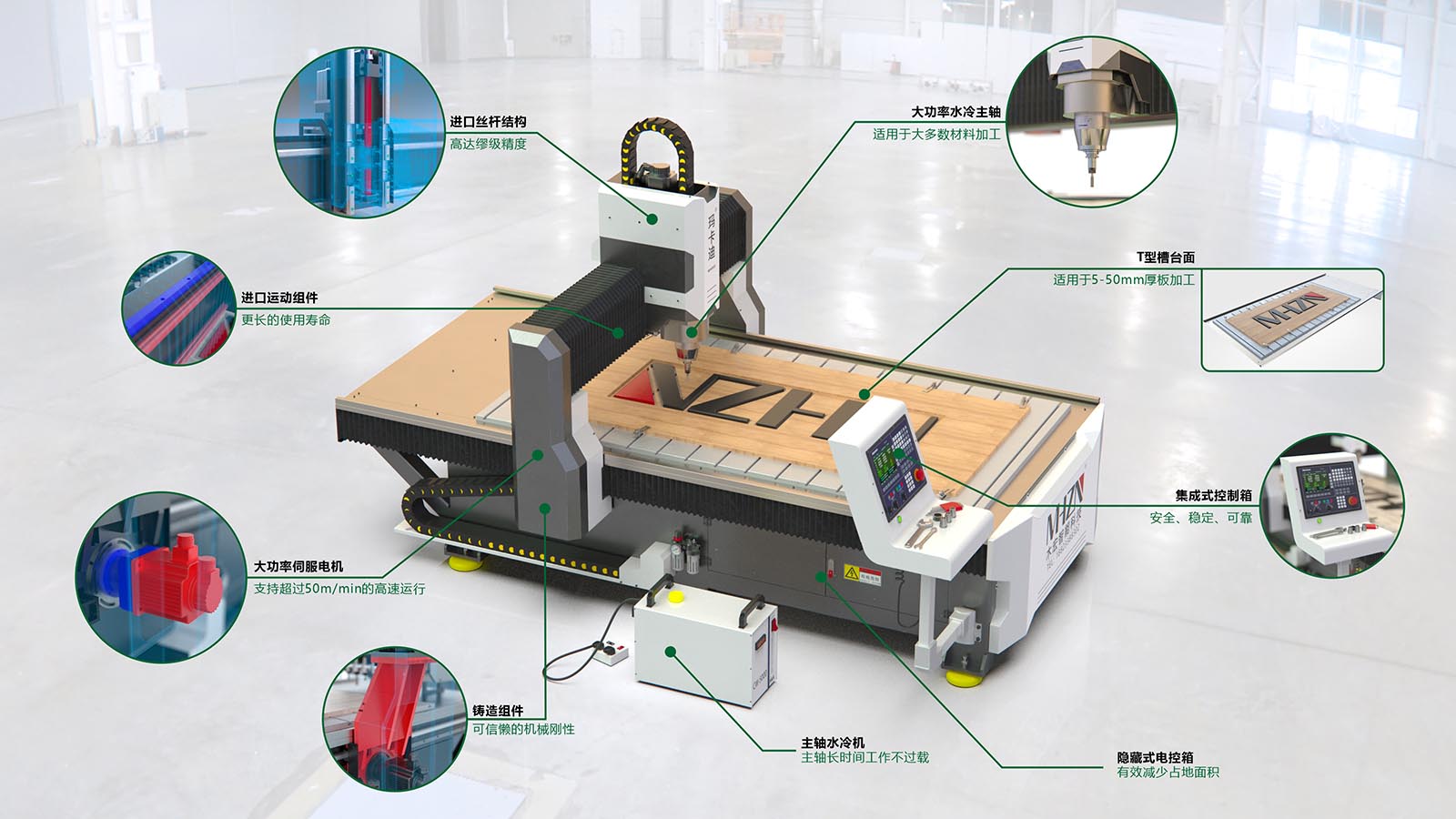
The structure and principle of explosion-proof AC servo motor
In single-phase asynchronous explosion-proof servo motors, special motors account for a large proportion, and their structures have their own characteristics and many forms. But in terms of its commonality, the structure of the motor consists of fixed parts...
In single-phase asynchronous explosion-proof servo motors, special motors account for a large proportion, and their structures have their own characteristics and many forms. However, in terms of its commonality, the structure of the motor is composed of three parts--- such as fixed part stator, rotating part---- rotor, support part--- end cover and bearing.
Explosion-proof AC servo motors are usually single-phase asynchronous motors, with two structural forms: squirrel cage rotor and cup rotor. Like ordinary motors, AC servo motors consist of stator and rotor. There are two windings on the stator, namely the excitation winding and the control winding, and the two windings differ by 90° electrical angle in space. The base that holds and protects the stator is generally made of duralumin or stainless steel. The rotor of the cage rotor AC servo motor is the same as that of a normal three-phase cage motor. The structure of the cup rotor AC servo motor is composed of three parts: external stator, cup rotor and inner stator. Its external stator is the same as the cage rotor AC servo motor, and the rotor is made of a non-magnetic conductive material (such as copper or aluminum) in the shape of a hollow cup, and the bottom of the cup is fixed on the shaft 7. The walls of the hollow cup are thin (less than 0.5mm), so the moment of inertia is small. The inner stator is made of silicon steel sheets stacked and fixed on an end cover, and there is no winding on the inner stator, which is only used for magnetic circuits. When the motor is working, neither the inner nor outer stator moves, and only the cup-shaped rotor rotates in the air gap between the inner and outer stator. For AC servo motors with small output power, the excitation winding and control winding are often placed in the grooves of the inner and outer stator cores.
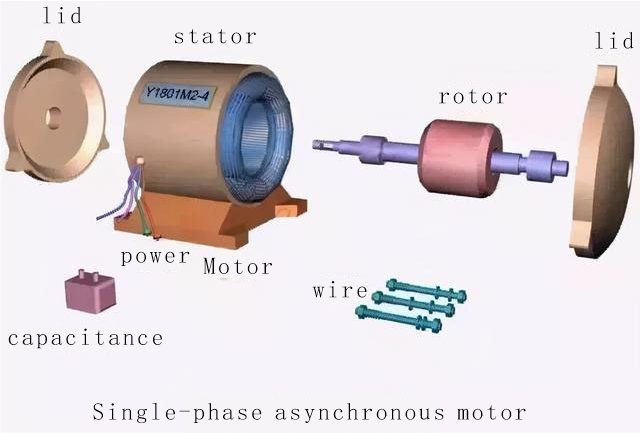
The main components of the motor include: 1. Base; 2. Iron core; 3. Winding; 4. End cover; 5. Bearings; 6. Centrifugal switch or starting relay and PTC starter; 7. Nameplate.
1. Machine base
The structure of the base varies with the motor cooling method, protection type, installation method and purpose. According to its material classification, there are cast iron, cast aluminum and steel plate structure. Cast iron base with heat dissipation ribs. The base is connected to the end cover and fastened with bolts. Cast aluminum machine bases generally do not have heat dissipation ribs. The steel plate structure base is made of thin steel plate with a thickness of 1.5-2.5 mm, welded, and then welded to the foot of the steel plate stamping parts. Some special motors have a rather special base, such as refrigerator motors, which are usually packed in a sealed tank with the compressor. The motor of the washing machine, including the motor of the spin dryer, has no base, and the end cover is directly fixed to the stator core.
2. Iron core
The iron core includes the stator core and the rotor core, which acts the same as the three-phase asynchronous motor and is used to form the magnetic circuit of the motor.
3. Winding
The stator winding of single-phase asynchronous motor is often made into two phases: the main winding (working winding) and the secondary winding (starting winding). The central axis of the two windings is staggered at a certain electrical angle. The purpose is to improve startup and operational performance. The stator winding is mostly wound with high-strength polyurethane enameled wire.
The rotor winding generally adopts a cage winding. Commonly used aluminum die-casting.
4. End cap
Corresponding to different base materials, end covers also have cast iron, aluminum and steel stamping parts.
5. Bearings
The bearingsare ball bearings and oil-impregnated bearings.
6. Centrifugal switch or starting relay and PTC starter
(1) Centrifugal switch
In single-phase asynchronous motors, in addition to capacitor runningmotors, in the starting process, when the rotor speed reaches about 70% of the synchronous speed, it is often with the help of centrifugal switches to cut off the starting winding of single-phase resistance starting asynchronous motor and capacitor starting asynchronous motor, or cutting off the starting capacitor of starting and running asynchronous motor. The centrifugal switch is generally installed on the inside of the shaft extension end cover.
(2) Starting relay
Some motors,such as refrigerator motors, are replaced by starting relays because they are assembled with the compressor and placed in a sealed jar, which is not convenient to install the centrifugal switch. The iron coil of the relay is connected in series in the main winding circuit, and when starting, the main winding current is very large, and the armature acts to close the moving contact in series in the secondary winding circuit. So the secondary winding is turned on, and the motor is in the two-phase winding running state. As the rotor speed rises, the main winding current continues to decrease, and the suction power of the attraction coil decreases. When a certain speed is reached, the suction force of the electromagnet is less than the tension of the reaction spring of the contact, the contact is opened, and the secondary winding is disconnected from the power supply.
(3) PTC starter
The latest starting element is the PTC, which is a thermistor that can be "on" or "off". PTC thermistors are a new type of semiconductor component that can be used as delayed starter switches. When in use, the PTC element is connected in series with the secondary winding of a capacitor-starting or resistive-starting motor. At the beginning of starting, because the PTC thermistor has not yet heated up, the resistance value is very low, the secondary winding is in the path state, and the motor starts to start. Over time, the speed of the motor continues to increase, the temperature of the PTC element rises due to its own Joule heat, when it exceeds the Curie point Tc (that is, the temperature point where the resistance increases sharply), the resistance increases sharply, and the secondary winding circuit is equivalent to disconnecting, but there is a small maintenance current, and there is a loss of 2-3 watts, so that the temperature of the PTC element is maintained above the Curie point Tc value. When the motor stops running, the temperature of the PTC element continues to drop, and its resistance value drops below the Tc point in about 2-3 minutes, at which time it can be restarted, which is exactly the downtime between the two start-ups stipulated by the refrigerator and the air conditioner.
Advantages of PTC starter: no contact, reliable operation, no noise and no electric spark, good fireproof and explosion-proof performance. And vibration resistance, shock resistance, small size, light weight, low price.
7. Nameplate
Including: motor name, model, standard number, manufacturer name, factory number, rated voltage, rated power, rated current, rated speed, winding connection, insulation level, etc.